Please 更新浏览器.
Findings
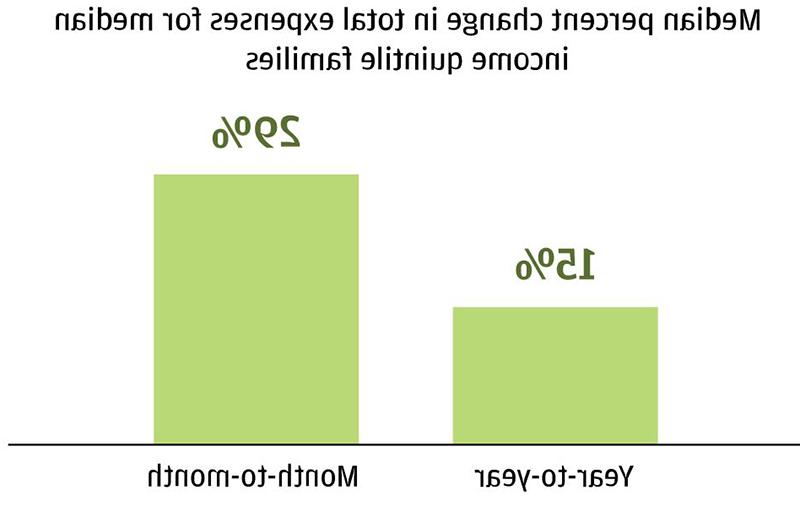
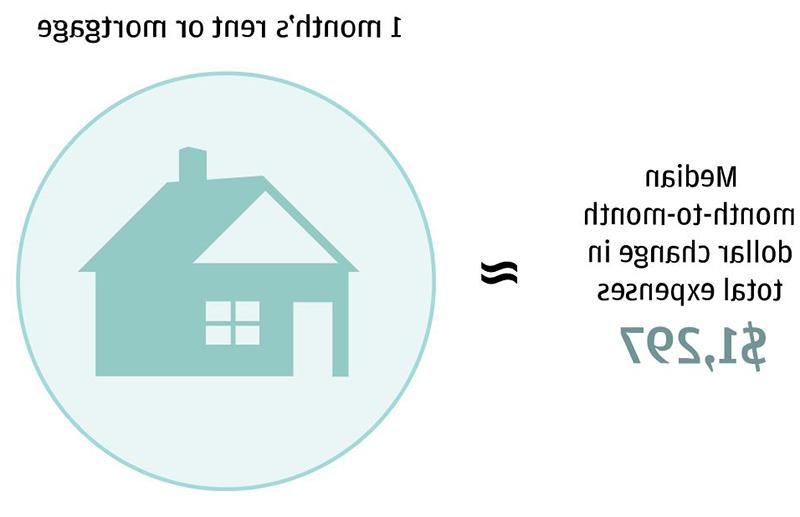
- 去找1费用上下波动近1美元,对于中等收入家庭,按月计算是300或29%.
- 去找2在收入和年龄范围内,费用波动率都很高. 而年龄较大的家庭通常收入波动较小, 他们的收入和支出波动幅度更大.
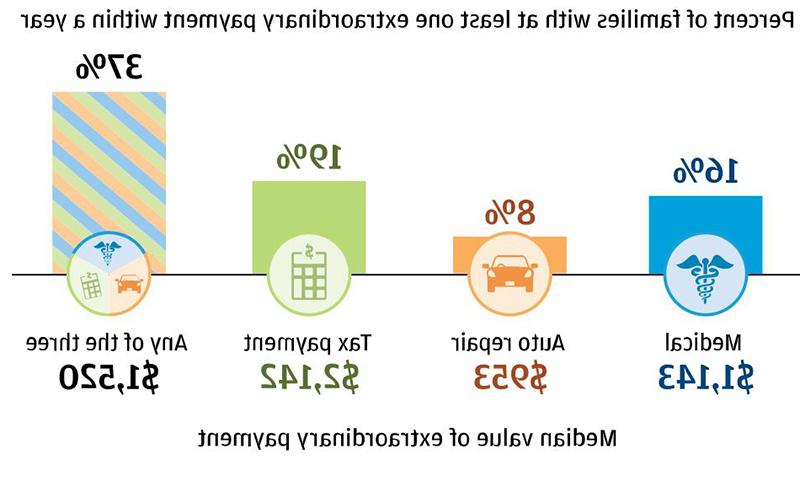
- 去找3Almost four in ten families—particularly middle-income and older families—made an extraordinary payment of over $1,500个与医疗服务有关, auto repair, or taxes.
- 去找4Extraordinary medical payments were more likely to occur in months with higher income and 具体地说 during tax season.
- 去找5在支付大笔医疗费用之前, families garnered significant 流动资产 but did not recover financially within 12 months after the payment.
Download
Americans across the income spectrum experience tremendous income and expense volatility, 而且这种波动性一直在上升. 这种波动考验着美国家庭的财务弹性. 风化挥发性, 我们估计中等收入家庭需要4美元,800 in 流动资产 to weather 90 percent of the income and expense volatility observed, 但他们只有3美元,2000美元——缺口1美元,800. 在工资, Paydays, and the Online Platform Economy we documented that most income volatility stems from labor income and, 具体地说, 一份工作中实得工资的变化,而不是工作的转换.
在这份报告中, the 12bet官方 Institute assembled a de-identified data asset of nearly 250,000 Chase customers between 2013 and 2015 in order to study how consumers’ expenses vary over time and how their financial behavior changes when faced with extraordinary payments. This high-frequency panel of family finances—weighted to represent the age and income distribution of the nation—provides a first ever look into the components of expense volatility based on real financial transactions and the changes to family income, expenses, assets, 以及伴随高额医疗费用而来的负债.
找到一个: 费用上下波动近1美元,对于中等收入家庭,按月计算是300或29%.
发现三: Almost four in ten families—particularly middle-income and older families—made an extraordinary payment of over $1,500个与医疗服务有关, auto repair, or taxes.
发现四: Extraordinary medical payments were more likely to occur in months with higher income and 具体地说 during tax season.
Extraordinary medical payments were more likely to occur in months with higher income. Total income was $163 or 4 percent higher in months with a major medical payment. The income increase stemmed mostly from tax refunds and not labor income and was still small in magnitude compared to the mean medical payment of $2,089.
Data
从3500万的支票账户客户中, 我们组装了一个由大约250个数据组成的去识别数据资产,000 core Chase customers for whom we could categorize at least 80 percent of expenses. 这些家庭符合以下五项抽样标准:
Conclusion
These findings highlight the critical role 流动资产 play in managing expense spikes and the need for policies and solutions to promote emergency savings. While many families experienced an increase in income in the month in which they made a major medical payment, 流动资产 were the primary source of funding to cover the medical payment. Our evidence also underscores the connections between financial health and physical health. 首先,医疗付款的时间与支付能力挂钩. Families may have delayed either medical treatment or payment of their medical bill until they were able to pay. The second link is that major medical payments were associated with lower income, 非医疗费用, 一年后,流动资产和更高的信用卡债务. This highlights the reality that families are not fully insured against the economic consequences of major health events. Older families in particular could benefit from more customized solutions as they exhibited a greater range in income and expense volatility and were also more likely to make major medical payments. 更广泛地说, better solutions could help families accumulate 流动资产 and predict, manage, 并负担得起费用飙升. Integrated, 收入高频数据, expenses, assets, 和负债 shed new light on expense volatility and how behavior changes with this volatility. This is critical to improving policies and solutions to strengthen the financial resilience of American families.